The Lake Winnipeg Aquarium
Inhabitants:
The Aquarium Side
(Lake Winnipeg)
Brown Bullhead
Characteristics - olive to brown with dark mottlings on sides, fading to white or cream underneath; fleshy barbels dusty to black; 22-23 rays in anal fin; caudal fin slightly notched.
Distribution - rivers in the southern portions of the province.
Foods - crayfish, aquatic invertebrates, other fish.
Other names -- bullhead, brown bullhead, mud puppies.
The brown bullhead is widely distributed in the southern part of the province, where it is common. Most major tributaries of the larger southern lakes hold stable populations. These fish are "fodder" for many other species in theses southern waters. eg. Walleye do key on them at certain times of the year in particular Manitoba watersheds. The brown bullhead is taken most commonly in the Red, Assiniboine, Whitemud and Winnipeg rivers.
Feshwater Drum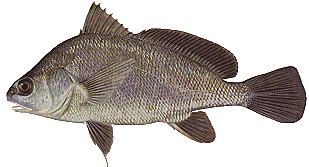
Characteristics - deep bodied, silvery fish; head and body slope steeply up from the snout and dorsal fin; long dorsal fin divided into two lobes; commonly weigh up to 5 lbs.
Distribution - rivers, and Manitoba's larger lakes.
Foods - fish, crayfish, immature insects
Other names-- sheepshead, silver bass
The freshwater drum is a common fish species in the Red and Assiniboine rivers and a large number of streams/rivers that flow into Lake Manitoba. Drum are very tolerant of turbidity and prefer quiet waters without swift currents. They are however very tolerant to current and have adapted to rivers with good current.
The drumming sound made when the fish is handled is produced by a special apparatus that is located in the body cavity, which is connected with the swim bladder. Two enlongated muscles move a tendon over the swim bladder and produce the sound.
Rock Bass 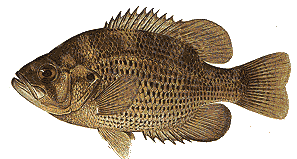
Characteristics - olive colored with brassy reflections and dark mottlings along the sides, whitish breast and belly; 6 spines in anal fin and 12 in the dorsal; they do exceed 10 inches in Manitoba and as such are a trophy. Foods - aquatic insects, minnows and other small fish.
Other names -- redeye bass.
Occurrence of this species occurs in clearer, rockier habitats of small rivers. Rock bass are also found in the rivers eg. the Assiniboine, Little Saskatchewan. Occasionally they are found in large, natural lakes and impoundments such as Lake of the Prairies and Lake Wanapotah.
Yellow Perch
Characteristics - sides bright yellow to brassy green with 7 dark vertical bars; lighter belly and dark olive green back.
Distribution - Province wide, greatest abundance in natural lakes.
Foods - small fishes, aquatic insects, small crayfish and snails.
Other names -- "Little Thieves"
The yellow perch is essentially a lake inhabitant in Manitoba and reaches its greatest abundance in the natural lakes. It is rarely found in large numbers in flowing water with the exception of smaller slower moving rivers in eastern Manitoba where it is common in some localities. They are also found in a number of man-made recreational lakes and river impoundments.
Sauger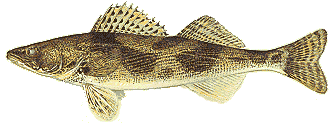
Characteristics - usually olive-gray on back with white belly; back crossed with 3-4 dark saddles extending down sides; 2-3 rows of black dots on the anterior dorsal fin; large, glossy eyes and sharp teeth; seldom exceeding 2-3 lbs.
Distribution - Same areas that walleyes would inhabit.
Foods - fish, other aquatic animals.
Other names -- Little sauger, gray sauger
The sauger is not choosy in its choice of clear waters and is often found in muddy rivers. It has a definite preference for larger rivers and spends much of its life there except during the spawning season, when it ascends tributary streams or enters backwaters in search of suitable spawning habitat.
The Marsh Side
(Grand Beach Lagoon)
Painted Turtle
Painted turtles are the most widely distributed turtle in North America.
They live in permanent freshwater habitats such as ponds, lakes, marshes, sloughs, and creeks.
They spend time in the soft bottoms of these bodies of water as well as in the aquatic vegetation and in sunny basking spots on or near the water.
Great Plains Toad 
The Great Plains toad (Bufo cognatus) is a provincially Threatened amphibian found in grasslands and dry brushy areas of the central plains, from southern Canada to central Mexico. It is a relatively large toad, with a body length of up to 11 cm (4 inches). Its upper side ranges in colour from greyishyellow to light brown or green. It is covered with small tubercles or warts and large dark brown to olive blotches with well-defined white borders. Its underside is creamcoloured, usually with no markings.
Leopard Frog
Northern leopard frogs have a wide range of habitats. They are found in permanent ponds, swamps, marshes, and slow-moving streams throughout forest, open, and urban areas. They normally inhabit water bodies with abundant aquatic vegetation. They are well adapted to cold and can be found above 3,000 m (9,800 ft) asl. Males make a short snore-like call from water during spring and summer. The northern leopard frog breeds in the spring (March–June). Up to 6500 eggs are laid in water, and tadpoles complete development within the breeding pond. Tadpoles are light brown with black spots, and development takes 70–110 days, depending on conditions. Metamorph frogs are 2–3 cm (0.79–1.2 in) long and resemble the adult.
This species was once quite common through parts of western Canada and the United States until declines started occurring during the 1970s. Although the definitive cause of this decline is unknown, habitat loss and fragmentation, environmental contaminants, introduced fish, drought, and disease have been proposed as mechanisms of decline and are likely preventing species recovery in many areas. Many populations of northern leopard frogs have not yet recovered from these declines.
Shiner Minnows
Common Shiner (Notropis cornutus): These fish are one of the most common type of bait fish and are almost exclusively stream dwellers. The Common Shiner can be identified by the nine rays on its anal fin and terminal mouth. This minnow is typically bluish silver on the sides and greenish blue on the back., save for breeding season in which case the male gains a rose colored tail and anal fin. The Shiner grows about 5–10 cm (2–4 in) within one year and reach a size of 13 cm (5 in) at adulthood.[4] Another common "shiner" bait fish is the young version of the European chub (Leuciscus cephalus or Squalius cephaloides) which is quite easy to catch. Notropis potteri is known as the Chub Shiner.
Cray fish
Crayfish – also called crawfish or crawdads – are freshwater crustaceans resembling small lobsters, to which they are related; taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills and are found in bodies of water that do not freeze to the bottom. They are mostly found in brooks and streams where there is fresh water running, and which have shelter against predators. Most crayfish cannot tolerate polluted water, although some species such as the invasive Procambarus clarkii are hardier. Crayfish feed on living and dead animals and plants.
